Monday, 01. April 2019
Nebulized hypertonic saline (HS) is an effective approach in patients with CF in improving mucociliary clearance, lung function and quality of life.
The proposed mode of action of hyperosmolar agents such as HS is the restoration of the airway surface liquid layer in patients with high mucus content like in CF. But exact mechanism of action of HS remains to be elucidated.
In this study, Goralski et al.1 evaluated the effects of 7% HS on human bronchial epithelial HBE cells that exhibit a range of mucus concentration, spanning „normal” (2%) to muco-obstructive conditions (12%) like in CF. Considering the diversity of nebulizers on the market, the authors mimicked the clinically-relevant delivery rates of a jet nebulizer.
Aim of this study:
Studying the kinetics of HS on the airway surface liquid (ASL): comparing the effect of repeated doses and different delivery rates.
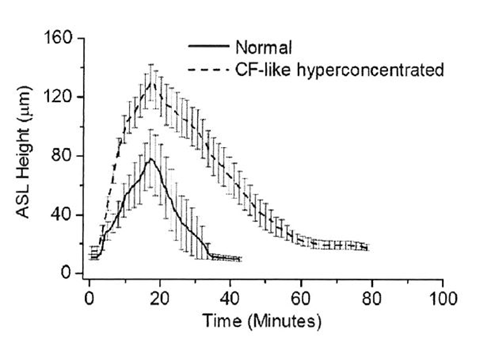
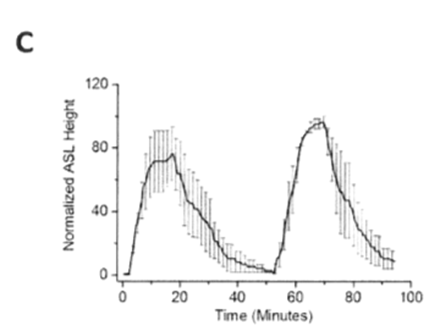
Tab. 1. HS was delivered to HBE cultures for 15 min at a rate of 8µg NaCl/cm2/min to mimic standard jet nebulizer delivery rate for human subjects
Conclusion:
1. Goralski JL, Wu D, Thelin WR, Boucher RC, Button B. The in vitro effect of nebulised hypertonic saline on human bronchial epithelium. Eur Respir J. 2018;51(5):1702652.
© 2025 PARI GmbH Spezialisten für effektive Inhalation